Earth’s magnetic field is defined by the North and South Poles that align generally with the axis of rotation (Figure 9.3.1 9.3. 1 ). The lines of magnetic force flow into Earth in the northern hemisphere and out of Earth in the southern hemisphere. Because of the shape of the field lines, the magnetic force trends at different angles to the
Convex & Concave Lens Ray Diagrams – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
ARTICLE Introducing magnetism Magnetism is a fascinating invisible force – it influences the environment around it. A magnet is a material that can pull certain types of metal towards itself … READ MORE MORE The Earth has a magnetic field extending thousands of kilometres into space. There is no big magnet inside the Earth.
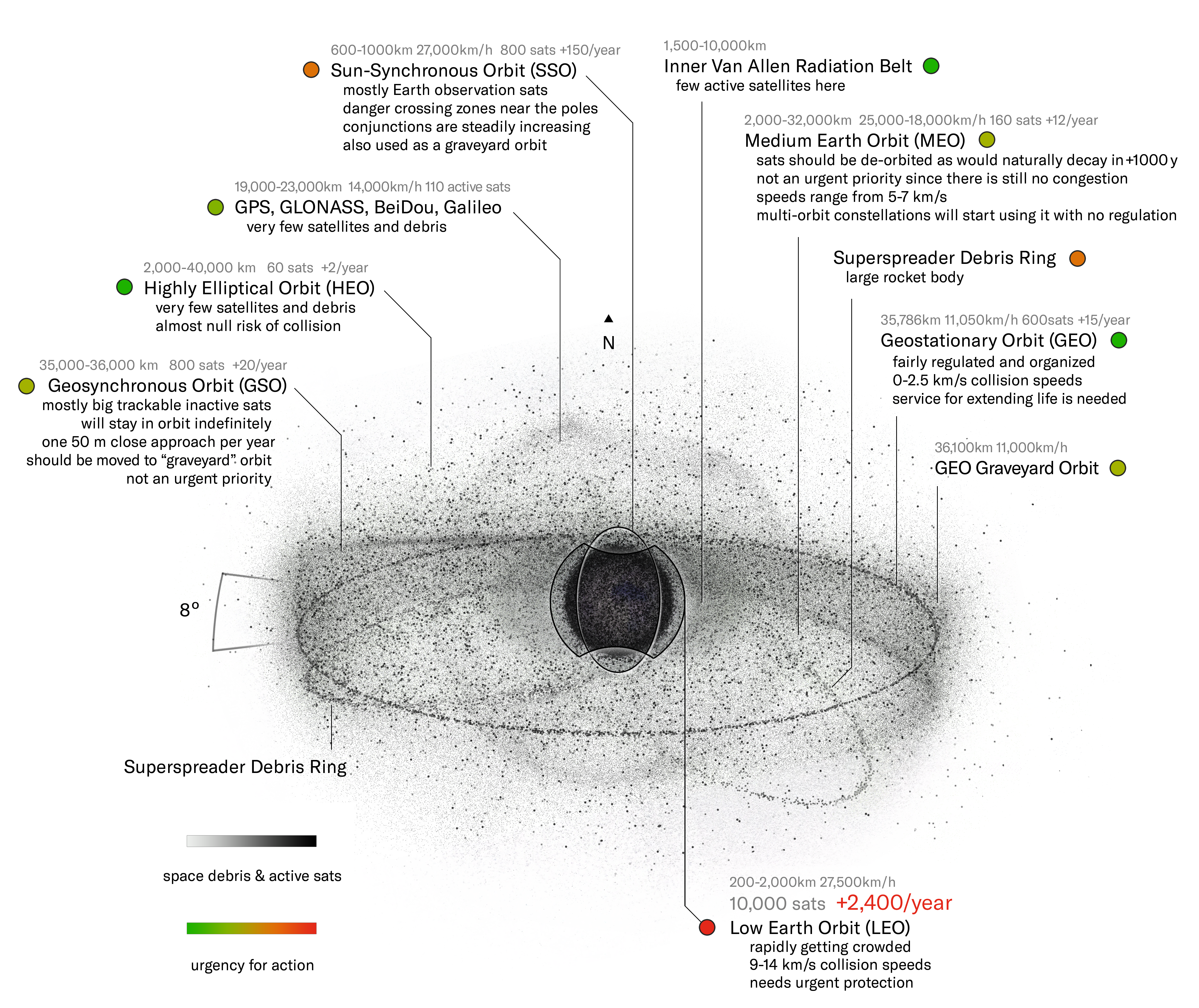
Source Image: en.wikipedia.org
Download Image
Jul 6, 2022Earth’s magnetic field can be visualized if you imagine a large bar magnet inside our planet, roughly aligned with Earth’s axis. Each end of the magnet lies relatively close (about 10 degrees) to

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
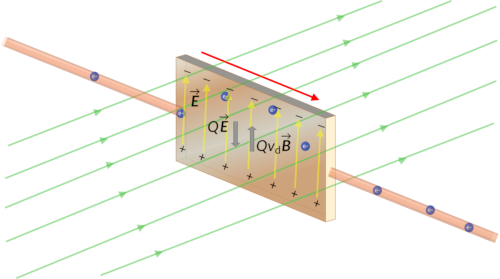
The Hall Effect | Physics | JoVE Laboratory Book: Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology (Deline, Harris & Tefend) 2: Earth’s Interior 2.4: Earth’s Magnetic Field
Source Image: jove.com
Download Image
Label The Diagram Of Earth’S Magnetic Field Appropriately.
Laboratory Book: Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology (Deline, Harris & Tefend) 2: Earth’s Interior 2.4: Earth’s Magnetic Field fl The Earth’s magnetic ßeld can be mapped by means of isomagnetic charts. These are explained on the next page. fl Secular variations are slow changes in the Earth’s magnetic ßeld with time. For example magnetic north drifts gradually over the years. fl Polarity reversals: There is very strong evidence from palaeomagnetism that the
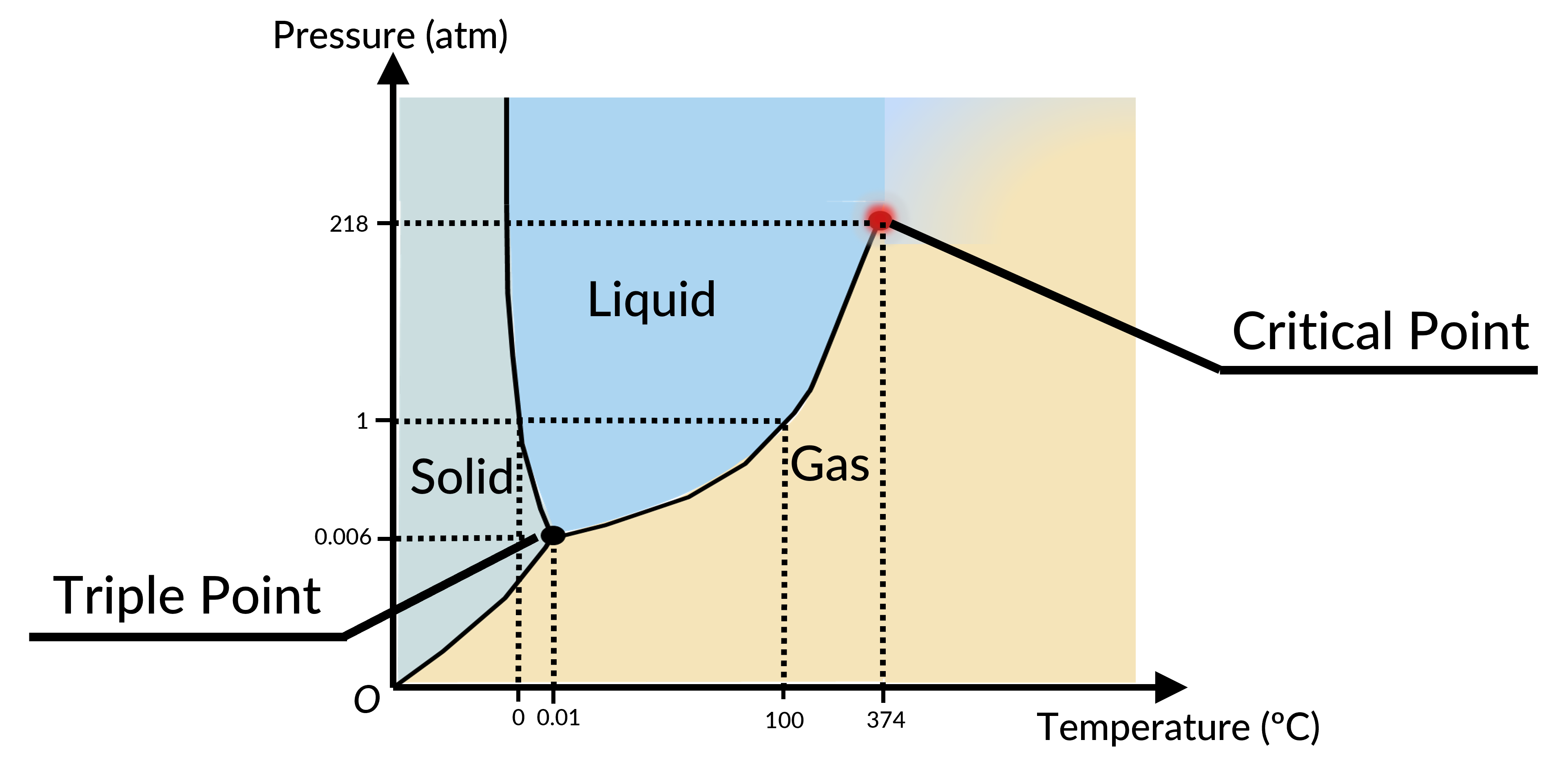
Phase Diagram | Physics | JoVE
Figure 9.15 Depiction of Earth’s magnetic field between reversals (left) and during a reversal (right). The lines represent magnetic field lines: blue where the field points toward Earth’s centre and yellow where it points away. The rotation axis of Earth is vertical, and the outline of the core is shown as a dashed white circle. Schematic diagram of the earth’s magnetic field (after Wiltschko and… | Download Scientific Diagram

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
4 steps to Numerical Modelling Best Practice – How-To & Guides Figure 9.15 Depiction of Earth’s magnetic field between reversals (left) and during a reversal (right). The lines represent magnetic field lines: blue where the field points toward Earth’s centre and yellow where it points away. The rotation axis of Earth is vertical, and the outline of the core is shown as a dashed white circle.
Source Image: seequent.com
Download Image
Convex & Concave Lens Ray Diagrams – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Earth’s magnetic field is defined by the North and South Poles that align generally with the axis of rotation (Figure 9.3.1 9.3. 1 ). The lines of magnetic force flow into Earth in the northern hemisphere and out of Earth in the southern hemisphere. Because of the shape of the field lines, the magnetic force trends at different angles to the

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
The Hall Effect | Physics | JoVE Jul 6, 2022Earth’s magnetic field can be visualized if you imagine a large bar magnet inside our planet, roughly aligned with Earth’s axis. Each end of the magnet lies relatively close (about 10 degrees) to
Source Image: jove.com
Download Image
Integrating over the Length of a Wire to Determine the Vector-Valued Force it Feels in a Uniform Magnetic Field | Physics | Study.com Nov 1, 2022This diagram illustrates how the Earth’s magnetic field can be approximated by that of a bar magnet. The blue axis represents the Earth’s rotational axis with the geographic North and South poles at top and bottom. The pink line represents the orientation of the bar magnet with North and South geomagnetic poles. Figure: JrPole, CC BY-SA 3.0.

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
How to Label a Phase Diagram | Chemistry | Study.com Laboratory Book: Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology (Deline, Harris & Tefend) 2: Earth’s Interior 2.4: Earth’s Magnetic Field

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Premium Vector | Earth’s magnetic field or geomagnetic field for education fl The Earth’s magnetic ßeld can be mapped by means of isomagnetic charts. These are explained on the next page. fl Secular variations are slow changes in the Earth’s magnetic ßeld with time. For example magnetic north drifts gradually over the years. fl Polarity reversals: There is very strong evidence from palaeomagnetism that the

Source Image: freepik.com
Download Image
4 steps to Numerical Modelling Best Practice – How-To & Guides
Premium Vector | Earth’s magnetic field or geomagnetic field for education ARTICLE Introducing magnetism Magnetism is a fascinating invisible force – it influences the environment around it. A magnet is a material that can pull certain types of metal towards itself … READ MORE MORE The Earth has a magnetic field extending thousands of kilometres into space. There is no big magnet inside the Earth.
The Hall Effect | Physics | JoVE How to Label a Phase Diagram | Chemistry | Study.com Nov 1, 2022This diagram illustrates how the Earth’s magnetic field can be approximated by that of a bar magnet. The blue axis represents the Earth’s rotational axis with the geographic North and South poles at top and bottom. The pink line represents the orientation of the bar magnet with North and South geomagnetic poles. Figure: JrPole, CC BY-SA 3.0.